Unleashing the Power of Managed DNS
A Comprehensive Guide to Enhanced Domain Management
Introduction:
In the digital era, where online presence is paramount, the Domain Name System (DNS) serves as the backbone, translating user-friendly domain names into IP addresses, the numbers computers and routers use to connect to each other. Managed DNS has emerged as a game-changer, offering businesses an efficient and reliable solution for domain management at scale. This comprehensive guide explores the compelling reasons why organizations of all sizes are opting for Managed DNS to streamline their online operations.
1. Reliability and High Availability:
- Advantage: Managed DNS providers typically operate on globally distributed networks, ensuring high availability for domain resolution and fast response times from anywhere. This translates to a consistent and reliable online presence, critical for businesses that cannot afford downtime or slow content loads.
2. Performance Optimization with Anycast:
- Advantage: Anycast technology employed by Managed DNS services routes DNS queries to the nearest available server. This reduces latency, optimizes performance, and enhances the overall responsiveness of websites and online services as well as dilutes DDoS attack traffic.
3. Scalability to Support Growth:
- Advantage: As businesses expand, so does the demand on DNS infrastructure. Managed DNS services are designed to scale seamlessly, accommodating the growing volume of DNS queries and ensuring that performance remains unhindered during periods of increased traffic. Most Managed DNS services also provide comprehensive API’s into their DNS and domain name platform which is critical for customers with tens of thousands of domain names or more.
4. Advanced Security Measures:
- Advantage: Managed DNS providers invest in robust security features, including DDoS protection and DNSSEC implementation. These measures fortify the DNS infrastructure against cyber threats, safeguarding the integrity and availability of domain names.
5. User-Friendly Management Interfaces:
- Advantage: Managed DNS services often come with intuitive interfaces, simplifying the configuration of DNS settings. This user-friendly approach allows individuals with varying levels of technical expertise to manage DNS records efficiently.
6. Automatic DNS Updates:
- Advantage: Automatic updates for DNS records are a hallmark of Managed DNS. This feature ensures that changes, such as IP address updates or new record additions, are propagated swiftly and accurately across the DNS infrastructure, reducing the risk of errors.
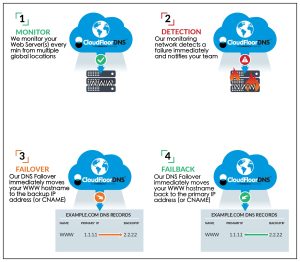
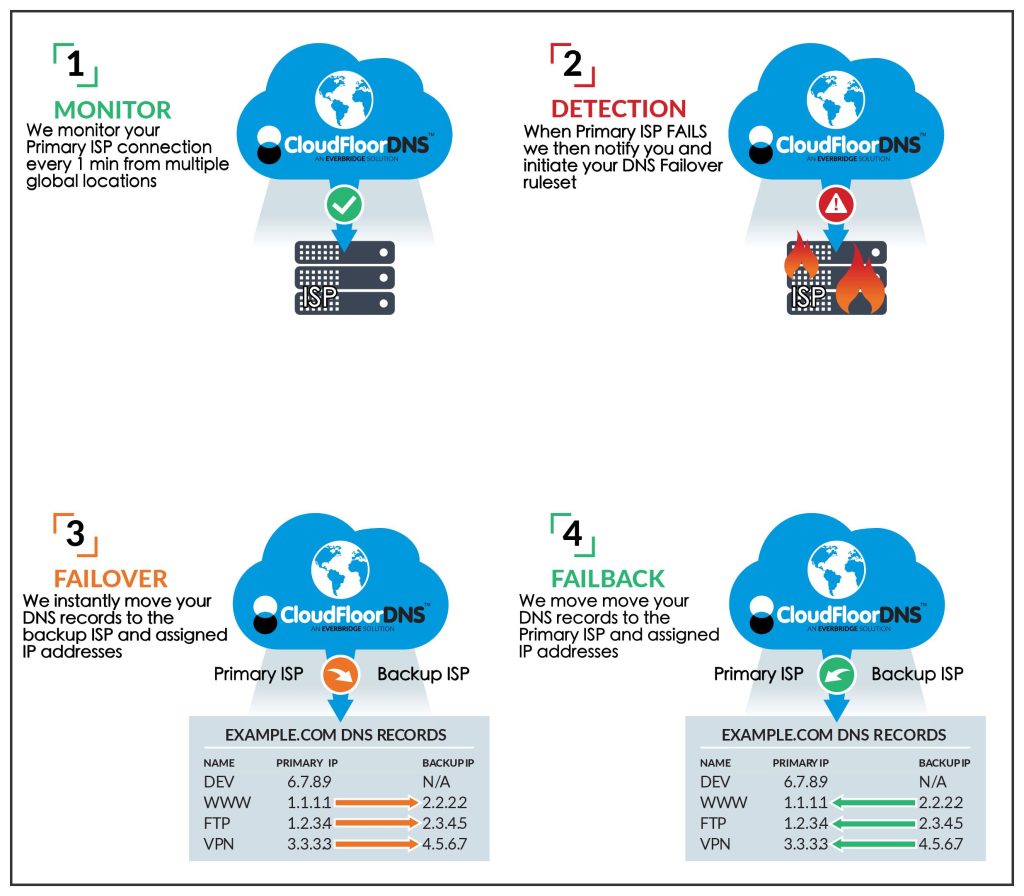
7. Redundancy and Failover Mechanisms:
- Advantage: Managed DNS providers implement redundancy in their infrastructure. In case of server failure or issues, traffic is automatically redirected to alternative servers, ensuring seamless continuity of service and minimizing downtime. This is an automatic feature when an Anycast DNS network is properly implemented.
8. Global Content Delivery for International Reach:
- Advantage: Managed DNS services with a global server network facilitate efficient content delivery worldwide. This is especially beneficial for organizations with an international audience, contributing to faster page loading times and an enhanced user experience. Custom Geographical DNS responses can also be implemented for international audiences, responding with localized content to their given region or country.
9. Dedicated Technical Support:
- Advantage: Managed DNS services typically include dedicated technical support. This valuable resource assists organizations in troubleshooting, optimizing DNS configurations, and maintaining the smooth operation of online services.
10. Focus on Core Competencies:
- Advantage: Outsourcing DNS management to a specialized provider allows organizations to focus on their core competencies. This is particularly beneficial for smaller teams or businesses without dedicated IT resources, leveraging the expertise of Managed DNS providers.
Conclusion:
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, Managed DNS emerges as a strategic choice for organizations seeking to optimize their online presence. The amalgamation of reliability, performance optimization, security features, and scalability positions Managed DNS as a comprehensive solution for efficient and hassle-free domain management. Whether for small businesses or large enterprises, embracing Managed DNS unleashes the power to enhance online reliability, security, and focus on core business objectives. As technology advances, leveraging Managed DNS becomes a pivotal step in ensuring a robust and future-ready online infrastructure.